
When the time comes to revoke the sudo privileges, simply rm the file for that user: # rm /etc/sudoers. This incident will be reported.Ĭan easily be given sudo access on a per-user basis: /root#. With this, an unprivileged user: /home/jim> sudo -i Printf '(username) will be given sudo privileges\n' Find a line which contains includedir /etc/sudoers.d. Then a script like this can be used to create a per-user sudoers file for any valid username: #/usr/bin/env bash This can be done is 3 quick steps: Edit sudoers file: sudo nano /etc/sudoers. So long as your sudoers file contains a line like: #includedir /etc/sudoers.d The sed command disables the #includedir directive that would allow any files in subdirectories to override these inline updates.Ī more modern method, given the age of this post, is to place a per-user file in /etc/sudoers.d/ or the appropriate similar location for whatever OS is at reference.The sed command does inline updates to the /etc/sudoers file to allow foo and root users passwordless access to the sudo group.The home directory is set to /home/foo.The uid and gid is set to the value of 999.The user foo is added to the both the foo and sudo group.Sed -i /etc/sudoers -re 's/^#includedir.*/# **Removed the include directive** #"/g' & \Įcho "foo ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL" > /etc/sudoers & \Įcho "Customized the sudoers file for passwordless access to the foo user!" & \

Sed -i /etc/sudoers -re 's/^root.*/root ALL=(ALL:ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL/g' & \ Sed -i /etc/sudoers -re 's/^%sudo.*/%sudo ALL=(ALL:ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL/g' & \ Groupadd -g 999 foo & useradd -u 999 -g foo -G sudo -m -s /bin/bash foo & \ Learn more about our VPS hosting services and Virtual private servers.Here's how I setup a non-root user with the base image of ubuntu:18.04: RUN \ Ready to get started with Passwordless Sudo in Linux? Get VPS Hosting from Atlantic.Net today!
CENTOS PASSWORDLESS SUDO HOW TO
In the above guide, you have learned how to configure passwordless sudo for a specific group, specific user and all users. Now, only the user can only run the “fdisk -l” command without a password. Save and close the file when you are finished. If you want to allow a specific user named vyom to execute only “fdisk -l” command without password, edit the /etc/sudoers file: nano /etc/sudoersĪdd the following line at the end of the file: your_username ALL=(ALL:ALL) NOPASSWD: /sbin/fdisk -l Replace it with the following line: %sudo ALL=(ALL:ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL Step 5 – Configure Passwordless Sudo For Specific User to Execute Only Specific Command
CENTOS PASSWORDLESS SUDO PASSWORD
If you want to allow all users to execute sudo without a password (note: this is only advisable in test systems and should never be used on production workloads), edit the /etc/sudoers file: nano /etc/sudoersįind the following line: %sudo ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL Step 4 – Configure Passwordless Sudo For All Users If you want to allow a member of a specific group named www-data to execute sudo without a password, edit the /etc/sudoers file: nano /etc/sudoersĪdd the following line at the end of the file: %www-data ALL=(ALL:ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL Step 3 – Configure Passwordless Sudo For a Specific Group You don’t need to provide any password after running the above command. Then, run any superuser command with sudo: sudo fdisk -l If you want to allow a user named vyom to execute sudo without a password, edit the /etc/sudoers file: nano /etc/sudoersĪdd the following line at the end of the file: your_username ALL=(ALL:ALL) NOPASSWD:ALLįor example: Atlantic-Admin ALL=(ALL:ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL
CENTOS PASSWORDLESS SUDO UPDATE
apt-get update -y Step 2 – Configure Passwordless Sudo For a Specific User Once you are logged into your Ubuntu 18.04 server, run the following command to update your base system with the latest available packages.
Connect to your Cloud Server via SSH and log in using the credentials highlighted at the top of the page. Create a new server, choosing Ubuntu 18.04 as the operating system with at least 1GB RAM. Step 1 – Create Atlantic.Net Cloud Serverįirst, log in to your Atlantic.Net Cloud Server. A root password configured on your server.A fresh Ubuntu 18.04 VPS on the Atlantic.Net Cloud Platform.In this tutorial, we will show you how to set up Passwordless Sudo in Linux. However, there is a great way to securely configure a passwordless sudo account Every time you sudo a sudo command you will be prompted for the sudoer password, which can become repetitive.

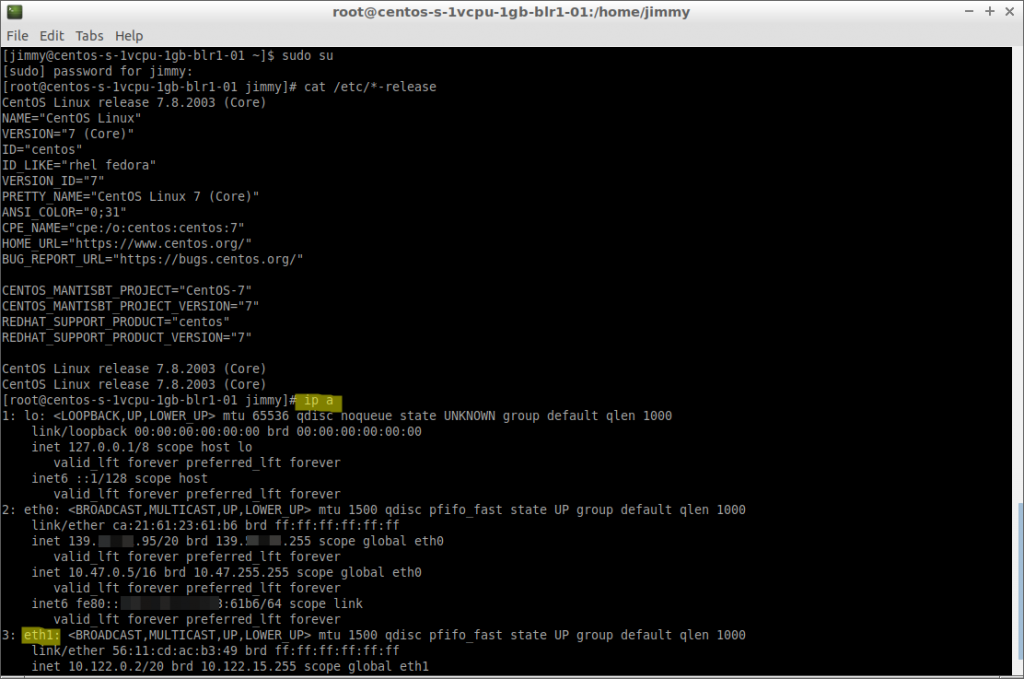
The sudo command elevates a standard user account, granting root access to the system. WIth sudo -s you may not get the extra system path for root. With your setup, you could do something like sudo su and it wont ask for a password. A standard user account only has limited privileges and can run only specific commands on the system. sudo and su are two different commands, and do different things. In a Linux system, the root user is a superuser that has permission to access everything on the server.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
